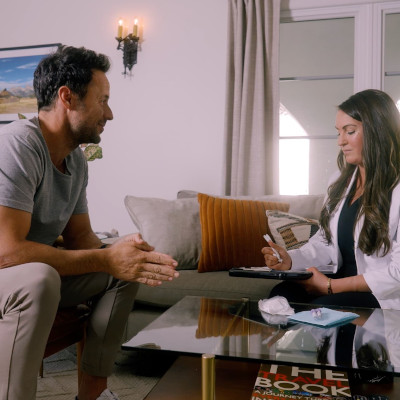
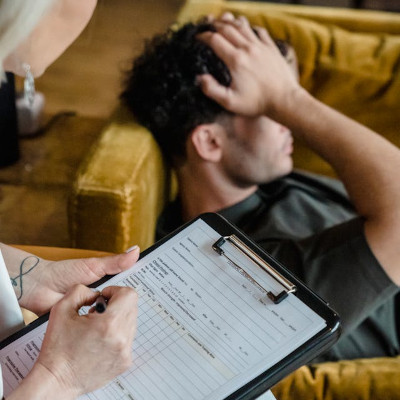
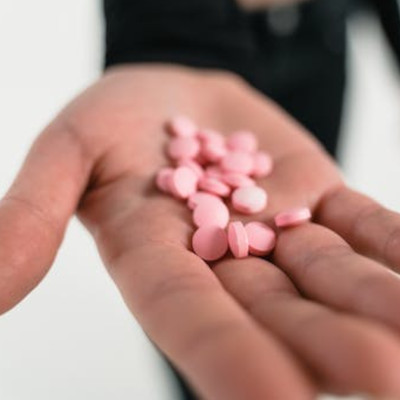
27 May Benefits of In-Home Alcohol Detox: Privacy, Comfort, and Personalized Care at Your Doorstep
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is a brain and memory disorder that can be caused by excessive alcohol use. Learn about its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and outlook....